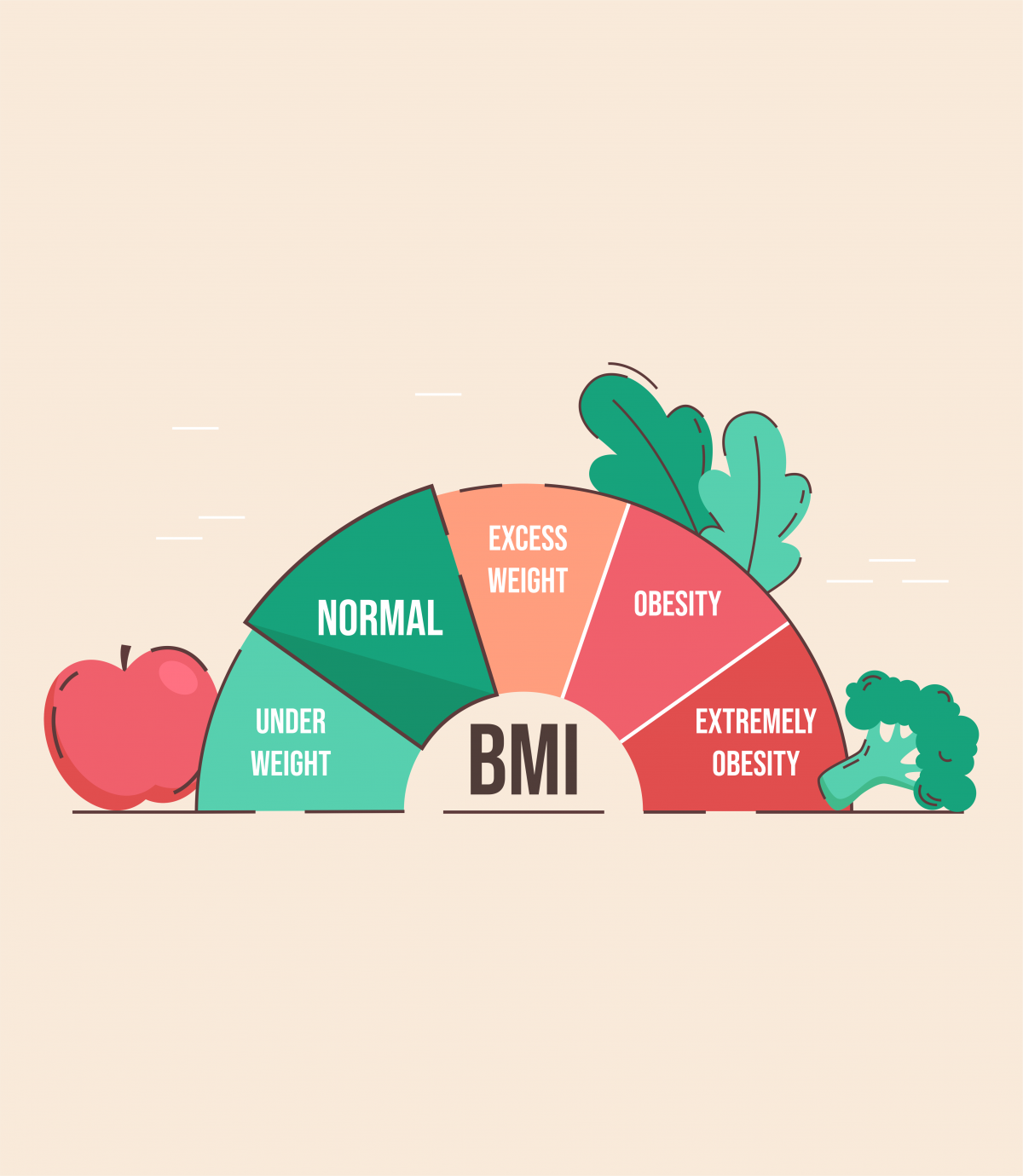
What is BMI?
Body mass index (BMI) is a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. BMI screens for weight categories that may lead to health problems, but it does not diagnose the health of an individual.
Is BMI an accurate method?
BMI is a highly inaccurate method. It is an unreliable indicator of body fat content which ignores factors such as muscle mass, bone density, general body composition, and variances in racial and gender makeup. The skeletal system is mostly disregarded. A person’s physical structure is extremely important. It is crucial to consider genetics as well and a person may already have certain medical conditions which can vary their weight drastically.
BMI and social stigma around weight?
BMI creates a social stigma around bodies and weight. BMI fixates on the ideology that shorter people need to have a thinner frame and taller people need to have a broader frame. This often leads to insecurity especially in children because every comment on their bodies can get to them easily. It ignores the activeness level of an individual. Another drawback of BMI is that while it can be used for the detection of diseases in the early stages it might lead to the wrong diagnosis.
The link between weight, muscle mass, and illness risk among various groups of people exhibit biological and genetic variations, which BMI does not consider. Compared to the general population, athletes often have a larger percentage of lean muscle mass and a lower percentage of fat mass. Their BMI measurements may be thrown off by these elements.
BMI is not a perfect measure of health and is often misleading. We need to reform the BMI structure or bring in a new method
